Department of Cortes
Cortés is one of the 18 departments that comprise the Republic of Honduras. Their administrative code is 05.
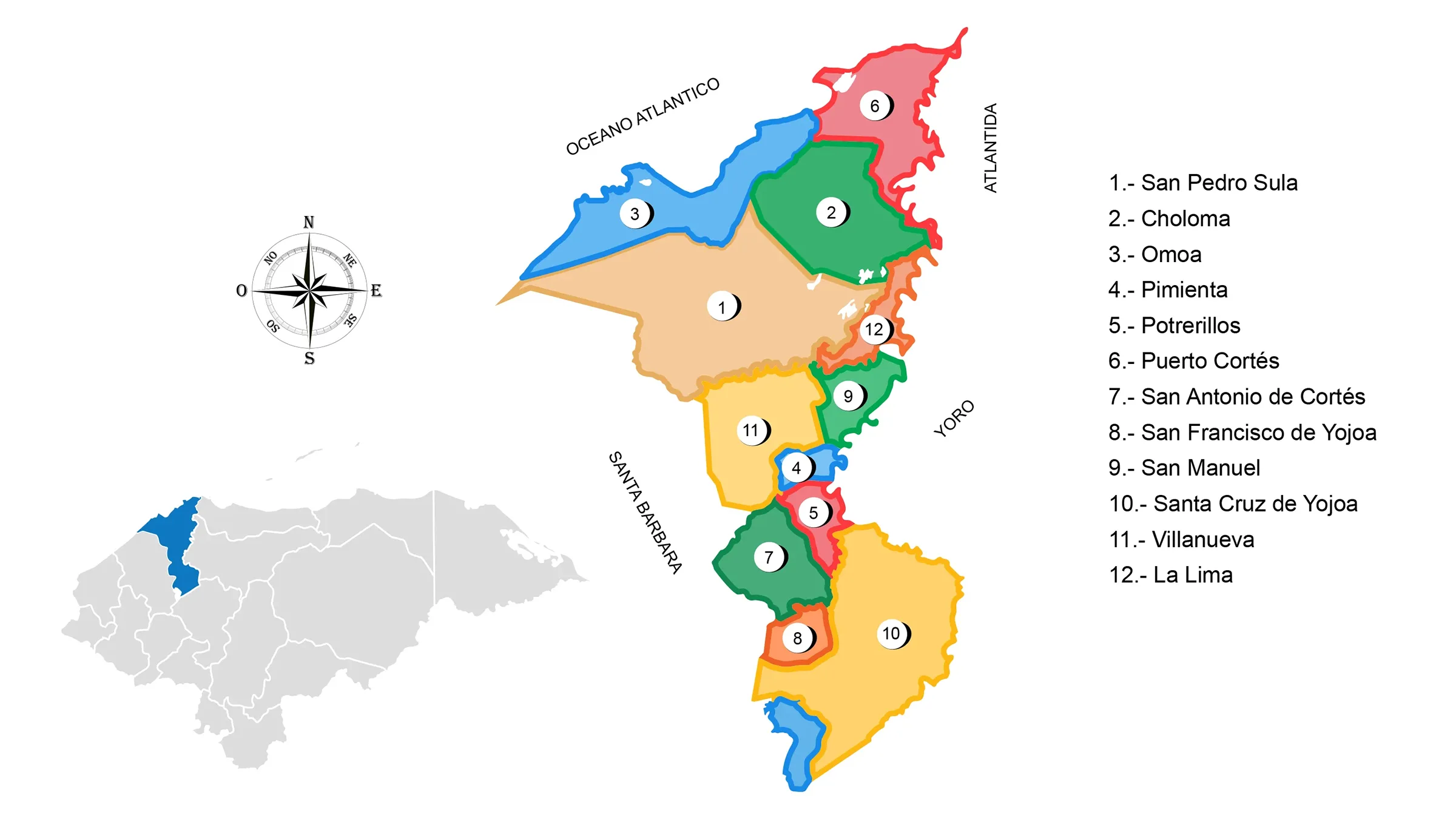
View Map of the Department of Cortés
General Information
Origin of its name: The department received its name in honor of the Spanish conquistador Don Hernán Cortés, who arrived in the territory of Honduras in 1525 and was the one who originally organized the conquest of the region.
Its departmental capital is the city of San Pedro Sula, the second most populous city in the country, also known as the «industrial capital of Honduras.» Origin of its name: In the Mesoamerican language, Xolometl maguey means «water of maguey.»
- Date of creation: July 4, 1893
- Departmental capital: San Pedro Sula
- Territorial area: 3,911 km2
- Administrative code: 05
- Municipalities: 12
- Aldeas: 284
- Total population (2018): 1,718,881
- Population in rural areas: 306,049
- Population in urban areas: 1,412,832
- Population density: 414.66 people/km2
- Life expectancy in years: 76.5
- Infant mortality rate: 12.8
History of Cortés
The first inhabitants of the Sula Valley and the territory of the current department of Cortés left archaeological evidence, including sites such as Naco, Playa de los Muertos, Cuyamel, and Cerro Palenque, belonging to the Lenca, Tolupan, Maya, and other cultures.
The arrival of the Spanish in the region dates back to 1524 with the explorer Gil Gonzáles Dávila, who founded the town of San Juan de Puerto de Caballos. It was the conquistador Pedro de Alvarado, along with his indigenous troops from the Achí tribe, who subdued the groups in the Sula Valley led by Cicumba in 1536, leading to the foundation of the town of San Pedro on June 27, 1536.
Colonial Era
During the colonial era, the city was attacked and burned by pirates seeking Spanish territories, limiting its development to commercial port activity between the interior and Puerto de Caballos.
It was a subdelegation under the province of Comayagua, with San Pedro Sula as its seat.
Creation of Cortés
The department was created on July 4, 1893, under the administration of Domingo Vásquez. This new department was created through a division from the department of Santa Bárbara.
It was formed by the districts of San Pedro Sula and Santa Crúz, which belonged to Santa Bárbara, and the districts of Tela and El Negrito, which belonged to Yoro. However, the latter two were annexed back to Yoro in 1894.
Cortés experienced economic growth with the arrival of North American fruit companies, as banana cultivation brought the installation of railways and shipping ports for the fruit. The department of Cortés is home to the country’s largest industrial development, and its capital, San Pedro Sula, is the second most important city, generating the highest fiscal revenues for the state.
Geography of Cortés
Location: It is situated in the northwestern part of the country.
View on Google Maps
Boundaries:
- North: Caribbean Sea
- South: Department of Comayagua
- East: Departments of Atlántida and Yoro
- West: Department of Santa Bárbara and the Republic of Guatemala
Municipalities of Cortés
See List of Municipalities in Honduras
- San Pedro Sula 0501
- Choloma 0502
- Omoa 0503
- Pimienta 0504
- Potrerillos 0505
- Puerto Cortés 0506
- San Antonio de Cortés 0507
- San Francisco de Yojoa 0508
- San Manuel 0509
- Santa Cruz de Yojoa 0510
- Villanueva 0511
- La Lima 0512
Climate of Cortés
The Department of Cortés has a warm and humid climate with temperatures ranging from 27°C to 30°C, and rainfall throughout the year, which maintains high humidity and stifling heat in the area.
The climate of Cortés is mild and humid, with a dry winter and a tropical rainy season. It has two distinct climatic zones: the Sula Valley and the surrounding mountainous areas. Precipitation varies as you move inland and along the shores of Lake Yojoa.
Topography of Cortés
Rivers of Cortés
Ulúa, Chamelecón, Jimerito, Cuyamelito, Santo Tomás, Ildefonso, Chiquito.
Lakes of Cortés
Laguna de Alvarado, Ticamaya, Jucutuma, and Lake Yojoa.
Protected Areas of Cortés
Cusuco National Park; multiple-use areas, Lake Yojoa; biological reserves, Motagua River Bar, and Zapatillos Keys.
Wildlife of Cortés
Mammals
- Shrew, squirrel, coatimundi, agouti, skunk, raccoon, deer, paca, tapir, peccary, coyote, foxes, wildcat, puma, ocelot, and jaguar.
Birds
- Woodpecker, dove, roadrunner, great-tailed grackle, seagull, pelican, mourning dove, parakeet, turquoise-browed motmot, thrush, heron, hawk, bearded vulture, owl, and fish eagle.
Marine Species
- Crab, lobster, dolphin, shark, shrimp, crab, stingray, and a variety of fish.
Flora of Cortés
- Coniferous forests in the mountains and mixed forests with broad-leaved trees in the coastal plain.
Economy of Cortés
Maquiladoras
San Pedro Sula, Puerto Cortés, Choloma, La Lima, Villanueva, Potrerillos, and Santa Cruz de Yojoa.
- Compañías operadoras de la zona industrial Río S.A. (SPS)
- Inversiones las Flores (Choloma)
- Parque industrial Real (Choloma)
- Parque industrial Triple A Ticamaya S.A. de C.V (Choloma)
- Villanueva Industrial Park (Villanueva)
- Zip Buena Vista (Villanueva)
- Zip Calpules (SPS)
- Zip Choloma (Choloma)
- Zip San Miguel (Choloma)
- Zona Libre América (SPS)
- Zona Libre Continental (La Lima)
- Zona Libre Honduras S.A. (Choloma)
- Zona Libre INHDELVA (Choloma)
- Zona Libre Zip San José (SPS)
Agricultural, Livestock, and Other Productions
Cultivation of bananas, plantains, sugarcane, African palm, oranges, cocoa, pineapple, cassava, corn, and rice; raising of cattle, sheep, and pigs; poultry farming; industries: textiles, food products, paper, beverages, tobacco, printing and publishing, chemicals, petroleum derivatives, basic metals, and manufacturing industries.
Mines
Gold, zinc, silver, antimony.
Emigration
The presence of maquiladoras stimulates internal migration to the department. This internal migration is often followed by emigration to Mexico and/or the United States of America.
Culture
Foods
- Grilled beef
- Grilled sausage
- Fried sausage
- Grilled pork
- Pressed meat
- Shredded beef
- Salpicón (finely chopped beef, condiments, spices, salt, and lime)
- Potato soup
- Bean soup with beef
- Bean soup with egg
- Chicken soup
- Conch soup
- Seafood soup
- Capirotada soup
- Mondongo soup
- Meatball soup
- Crab soup
- Clam soup
- Fresh fish soup
- Dried fish patty soup
- Tapado (stew) with pork and braised beef, with plantains, or boiled cassava, with coconut milk
- Yaguazo gumbo (wild duck)
- Ground beef patties
- Deer leg
- Stewed fish with camuleño plantains
- Stewed pork
- Casabe (cassava bread)
- Baleadas
- Montucas
- Fresh fish tapado
- Iguana or garrobo soup
- Fried mazapán
- Stuffed mazapán
- Paella rice
- Shrimp rice
- Fried beans
- Stewed beans
- Beans with rice
- Moronga or blood sausage
- Pork nacatamales
- Chicken nacatamales
- Meat pastries
- Stewed fish
- Fried fish with plantain slices
- Fried chicken with green banana slices
- Pork rinds and cheese pupusas
- Dried fish tapado
- Coconut beef tapado
- Ground beef patties
- Corn cakes
- Fish cakes
- Yucca with pork rinds
Beverages
- Corn atol
- Poleada (cornmeal pudding)
- Chilate
- Horchata (rice drink)
- Tamarind fresco
- Nance fresco
- Melon fresco
- Watermelon fresco
- Lemonade
- Punch
- Rompopo (eggnog)
Desserts
- Corn tamalitos
- Rice pudding
- Sweetened squash
- Sweetened plantains
- Torrejas (French toast)
- Plantain pudding
Tourism in Cortés
- San Fernando de Omoa Fortress
- Beaches of Puerto Cortés and Omoa
- Zapatillos Keys
- Historical museums
References
- Source: INE, Population Projections 2018. National Population and Housing Census 2013.


